Data Mapper
Syndesis have a data mapping step called Data Mapper.
Using AtlasMap, the Data Mapper interface opens up and shows all available data types to define mappings. Data Mapper can consume data from all previous steps, and produce an input for the next step.
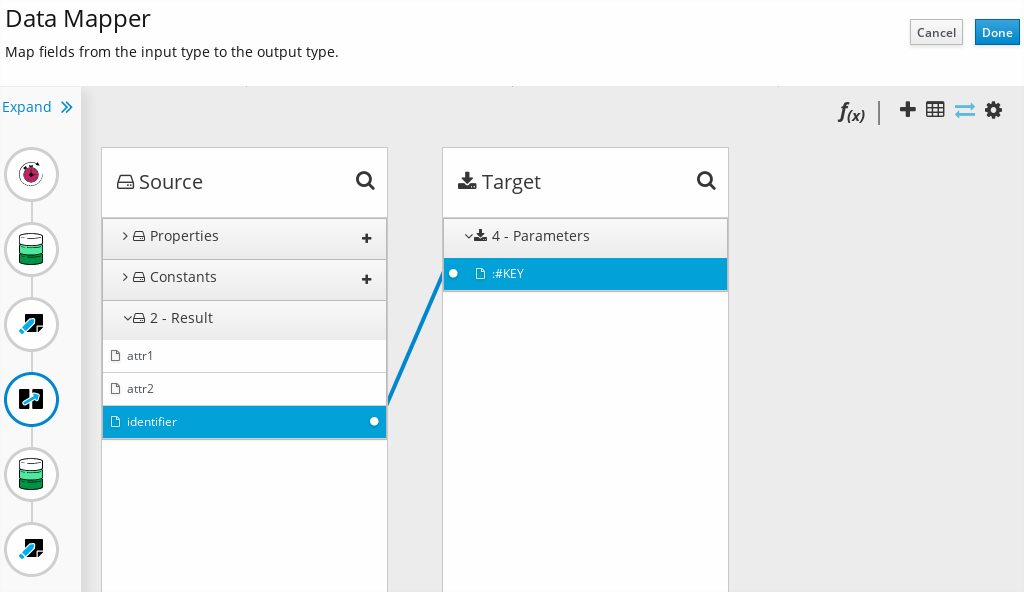
Figure 1. Data Mapper on Syndesis
Source documents are the input parameters for Data Mapper, which are the outputs from all previous steps. Target document is the output from Data Mapper, which is the input for the next step. Each document consists of fields, and the mappings are defined field by field.
In other words the Data Mapper is a tool to define and execute a set of field mappings. The Data Mapper step generates a mapping definition and store it as a part of the integration.
Basic field type conversion is applied automatically during executing mapping. You can also add more complex Transformations for each mapping.
Components
Data Mapper has three differentiated components:
User Interface
Data Mapper has a user interface to define data mappings. It interacts with the Design Runtime backend service.
You can define mappings in the UI by selecting source and target field(s), choose a mapping type, and add Transformations if needed.
Data Mapper Host Component integrates AtlasMap Data Mapper UI into Syndesis.
Design Runtime
Design Runtime is a REST service to be used by the Data Mapper user interface.
Data Mapper Design Runtime resides as a part of syndesis-server. It runs endpoints implemented as AtlasMap services:
The following types of API are provided:
Inspection
Inspection service consumes some kinds of data type definition and produce an unified internal format, called Document, which represents the data structure as a set of fields.
AtlasMap has several types of inspection service such as:
- Java: consumes fully qualified class name
- JSON Schema: consumes JSON Schema
- JSON Instance: consumes JSON instance document
- XML Schema: consumes XML Schema
- XML Instance: consumes XNL instance document
Validation
This service validates the mapping definition.
For example, when you define a Long => Integer mapping, the user interface requests to validate the mappings, and then the validation service detects a posibility to get the value out of range on that mapping. UI then returns a warning about a range concern.
Transformation (FieldAction)
Transformation is called FieldAction internally.
The FieldAction service returns a list of all available FieldAction details, including name and supported field type. The user interface then shows them as a list where the field type matches with the supported field type of the Transformation.
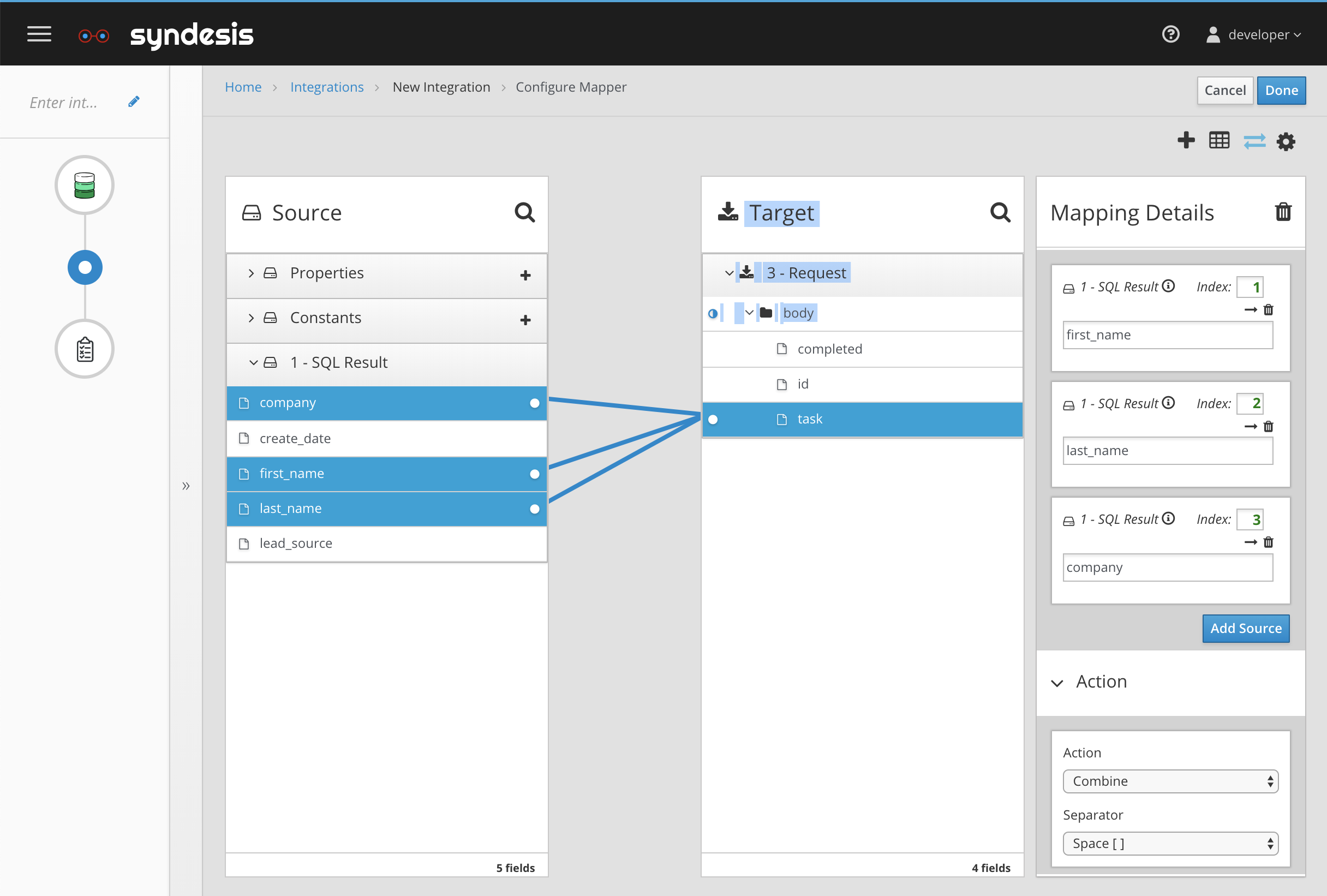 Figure 2. Data Mapper with Transformations
Figure 2. Data Mapper with Transformations
camel-atlasmap component
camel3-atlasmap component is an Apache Camel component to execute our mappings. It consumes a mapping definition file and a set of input data from Camel input messages, then performs mappings according to the provided mapping definition, produces an output and puts it into the output message of the step.
Data Mapper and DataShape
Each Syndesis Action has one Input DataShape and one Output DataShape. Data Mapper consumes these shapes to initialize Documents.
You can find more information on Datashapes on the DataShape section.
Camel Integration
In order to capture all the messages from previous steps for Data Mapper, Syndesis embeds an internal Camel processor.
This processor is invoked on each step defined in Syndesis. It captures the output message of each step and put it into the Message Map held as an Camel Exchange property. The Step ID is used as a key, allowing Data Mapper to link between the data type defined in each step and the actual message in the Message Map at runtime.
More information
You can find more information on this Data Mapper on the repository.